Amazon Heuristic Evaluation

A Heuristic Evaluation for the Amazon Mobile app following Jakob Neilsen's 10 Heuristics, and creating a design proposal for improvements.
Heuristic Evaluation/ App Redesign





Project Overview
Role:
UX/UI Designer
Project Type:
Heuristic Evaluation/ App Redesign
Timeline:
Two Weeks
Tools:
Figma
In Collaboration with two other UX Designers, we were tasked to evaluate the usability of an existing app or website and implement a redesigned user experience based on our findings from a Heuristic Evaluation.
My team and I decided to evaluate the very well known and frequently used Amazon Application in order to uncover usability issues and suggest design improvements that could improve the user experience.
This Heuristic Evaluation was in Collaboration with Yuri Shareef and James Rohan.
Platform:
IOS Mobile Application
What is a Heuristic Evaluation?
If you're not familiar, A Heuristic Evaluation is a method of identifying design problems within a user interface. Evaluators judge the design against a set of guidelines (called heuristics) and rank them on a severity scale from 1-4 (1 being not a problem and 4 being a major problem).
Jakob Neilson created these 10 principles for interaction design by basing them on understanding human behavior, psychology and information processing. Using these 10 heuristics to evaluate design can eliminate user deficiencies and help improve the overall design and user experience.
Jakob Nielson's Severity Scale
The Severity scale is a criteria recommended by Nielson that evaluates the severity of each Heuristic violation.
1
Cosmetic Problem
3
Major Usability Problem
0
Not a Problem
2
Minor Usability Problem
4
Usability Catastrophe!
This evaluation considers three main factors: Frequency, Impact and persistence. Having each Heuristic violation rated by this scale helps prioritize the impact on the user experience and in turn, helps communicate the impact and consequences of each violation to the company stakeholders.
User Task Flow
Amazon is a large platform with many different task flows. We decided to focus on one specific task flow so as not to overwhelm ourselves and because we believe searching for and buying an item is the primary task flow that most Amazon users take on a day-to-day basis.
Our Task Flow Included:

The Evaluation
By referencing the 10 principles of heuristic design we were able to identify five usability violations throughout our task flow. We placed these five violations on a prioritization matrix to prioritize our design solutions by value and effort. Although not all violations were severe, we were still able to recommend design solutions for each one.
We very much believe that if Amazon improved upon these five things within this task flow it would increase customers overall experience with the app and lead to an increase in customer retention and sales.
Heuristic Violation #1
Visibility of System Status
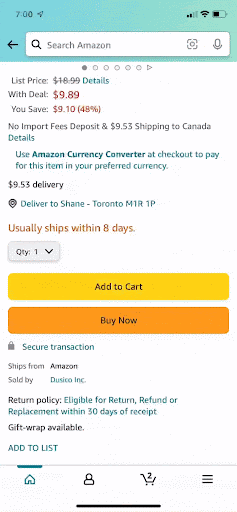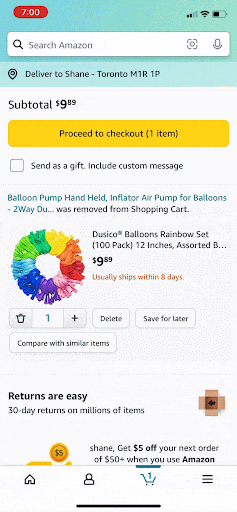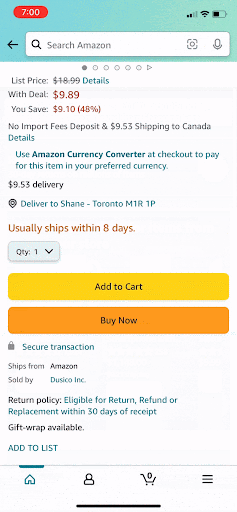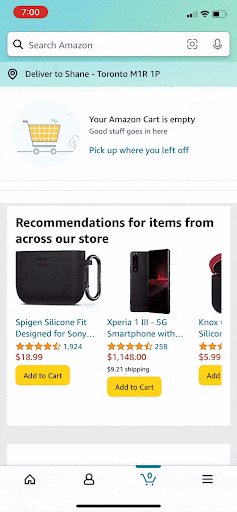
Issue: Deleting From Cart
After items are deleted the “empty cart” graphic does not appear until you click the home icon and then back to the cart. This makes it difficult to know if you’re items were successfully deleted.
Major Usability Problem
Severity Ranking
0
1
2
3
4
Have the empty cart graphic show immediately after the customer has deleted all items from their cart.
Recommendation
Before
After

Heuristic Violation #2
Error Prevention
Issue: "Proceed To Checkout" Placement
"Proceed To Checkout" is at the top of the page rather than below the items that are being purchased. This causes not much separation between what is in your cart vs promotions below and can lead to confusion of what the customer is actually purchasing
Minor Usability Problem
Severity Ranking
0
1
2
3
4
Place the checkout button and subtotal below the items being purchased to create a clear separation from the promoted items.
Recommendation
Before

After

Heuristic Violation #3
Recognition Rather Than Recall
Issue: Form Field Label Disappears
The labels indication what information needs to be given in the form field for "name" and "card number" dissapear after user begins typing which means the user has to delete what they type if they forget which information they need to input.
Minor Usability Problem
Severity Ranking
0
1
2
3
4
Have the form field labels above the text boxes to begin with so the user knows at all times exactly what information needs to be inputted.
Recommendation
Before

After

Heuristic Violation #4
Aesthetic And Minimalist Design
Issue: Inconsistency in labelling standard
The items listed on the results page do not adhere to a standard, the items do not follow a consistent labelling convention making the page look cluttered and hard to understand.
Minor Usability Problem
Severity Ranking
0
1
2
3
4
Have a clear hierarchy for the information listed on each item. Having more consistency in where similar items are grouped would create a more positive user experience as well.
Recommendation
Before
After


Heuristic Violation #5
Help Users Recognize, Diagnose and Recover from Errors
Issue: Inconsistent Error Messages
Only postal code and city receive an error message when input wrong. The boxes for phone number and address do not which could cause problems for the user if they type either wrong and do not catch the mistake themselves.
Major Usability Problem
Severity Ranking
0
1
2
3
4
Have the system be able to detect and show an error message when any information has been input incorrectly.
Recommendation
Before
After


The Next Steps
In our next steps, we would first look to evaluate the mobile application further to uncover heuristic violations not yet identified. Secondly, we believe that an evaluation of the Amazon website would be in order, to make the experience from web to mobile seamless. Lastly, we would implement our redesigns and collect qualitative and quantitative data to measure the success of said redesigns and the increase (or decrease) of customer retention.
Key Learnings
A Simple task isn't always simple
The task of finding an item and purchasing it may seem simple but because of the heuristic violations we found, it can easily confuse potential customers and take away from the shopping experience on Amazon. It is important to keep the actions on the user's end simple and easy to ensure a seamless experience.
UX Patterns can build upon consistency and standards
To improve a User Experience you don't have to completely change a design, by incorporating patterns and only changing what is necessary we were able to improve upon the already existing consistencies and standards
Working within established branding constraints
Adopting a brand's existing styles and UI libraries was a fun challenge, luckily we were all very familiar with Amazon's existing branding however this experience taught us to work within the given visual constraints so the end result is consistent and does not feel jarring amongst the rest of the application.
Let's Connect!
I am open to full-time positions in the UX/UI field located in Vancouver Canada or remote!


